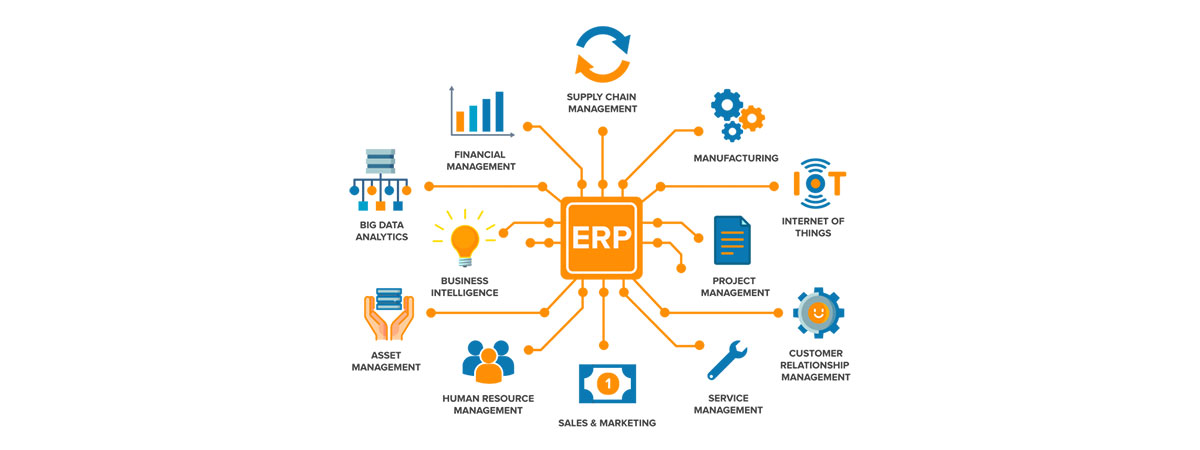
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a type of software that businesses use to increase organizational efficiency by managing their main business processes, often in real-time. ERP simplifies multiple systems, including supply chain, manufacturing, services, financial, accounting and procurement, project management, customer relationship management, risk management, compliance, and supply chain operations.
ERP systems are essential to companies because they bring together multiple business processes and allow data flow between them. By gathering an organization’s collective transactional data from various sources, ERP systems reduce data duplication and provide data reliability. ERP allows for data fields from all the sources in the organization to roll up to the proper account in the company’s general ledger so that all costs are accurately tracked and represented.
Costs of ERP Systems
However, ERP systems are known for being reasonably costly. This reputation of high cost is due to having a long and extensive process from development to deployment. Many companies require customizations from the Commercial of the Shelf (COTS) product to get the software to work for their business. Customizations, in turn, ramps up the ongoing maintenance costs, especially when upgrades are made to the system. The development process is time-consuming and complex, even if a company takes a minimal approach to customization.
Training large companies on new ERP systems that, in effect, have taken over the entire business process is costly. When new upgrades are implemented, either because of a standard system upgrade or a customer-requested upgrade, testing must commence, training manuals upgrades, and personnel trained. Support staff should be available and trained to assist personnel.
Are ERP systems worth the price?
Many companies have wondered if investing in an ERP system is worth the price while in the middle of implementation and before ever stepping into the development. However, for large companies, the benefits outweigh any headaches along the way. ERP systems can save substantial money by highlighting errors, freeing up resources, and performing routine tasks that can be easily automated, strengthen security, and allow companies to make wiser business decisions.
One of the main reasons an ERP system allows businesses to make more informed business decisions is the real-time data the ERP system provides. As data is shared in real-time across previously separated departments, companies find greater cooperation from co-workers sharing data in contracts, requisitions, and purchase orders. This information sharing results in increased productivity, cost savings, and improved ROI from the integration and automation that ERP software delivers.
Implementing an ERP system can take anywhere from a few months to a few years. This time difference varies dramatically depending on the company size, the number of modules or departments being integrated into the ERP system, the number of employees, whether the system will be configured and implemented in-house or contracted out, the integration of data legacy systems, and the training of employees. Generally speaking, it’s best to plan for more time to implement the system than less due to the complexity of ERP systems.
Types of ERP Systems
There are three types of ERP systems: on-premise, cloud, and hybrid. The type of system the client chooses is often dependent on upfront cost, on-site IT support capabilities, and long-term planning goals.
The traditional model of ERP system is an on-premise system where the client controls everything during deployment and throughout maintenance. The hardware and software are installed on-site, and the client maintains responsibility.
In a cloud ERP system, the system runs on the supplier’s cloud computing platform, and maintenance is provided by the supplier. The client has the option of choosing between a public or private-based cloud system. Many companies are merging from an on-premise ERP system to a cloud-based ERT system. This type of system requires an upgrade of their ERP system of different software and deployment options.
Hybrid ERP is also known as a two-tier ERP system. Companies use this combination system when their business requirements demand their data be both on-premise and in the cloud.
Overall Importance of ERP Implementation
Most important and often the most overlooked item on an ERP implementation schedule is the training of employees. Software, hardware, testing, and business requirements tend to receive months, if not years, of attention, while training of employees can simply be a line on the project plan.
Downplaying the training is where a lot of companies fail in their ERP system implementation. A successful system is only as good as user adoption and buy-in. Getting the ground floor users involved from the get-go and involving the training staff from the early stages will increase the odds of a successful ERP implementation.